Plant Molecular Biology 73: 67-87 (2010)
Cross-species approaches to seed dormancy and germination: conservation and biodiversity of ABA-regulated mechanisms and the Brassicaceae DOG1 genes
Botany / Plant Physiology, Institute for Biology II, Faculty of Biology, University of Freiburg, Schänzlestr. 1, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany, Web: 'The Seed Biology Place' http://www.seedbiology.de (K.G., A.L., K.M., A.R., G.L.-M.)
Department of Cell Biology and Genetics, Palacky University in Olomouc, Slechtitelu 11, 78371 Olomouc-Holice, Czech Republic, and Department of Botany and Plant Physiology, Mendel University of Agriculture and Forestry in Brno, Zemedelska 1, 61300 Brno, Czech Republic (A.W.)
Received August 28, 2009; Accepted November 22, 2009; Published online: December 15, 2009
DOI: 10.1007/s11103-009-9583-x
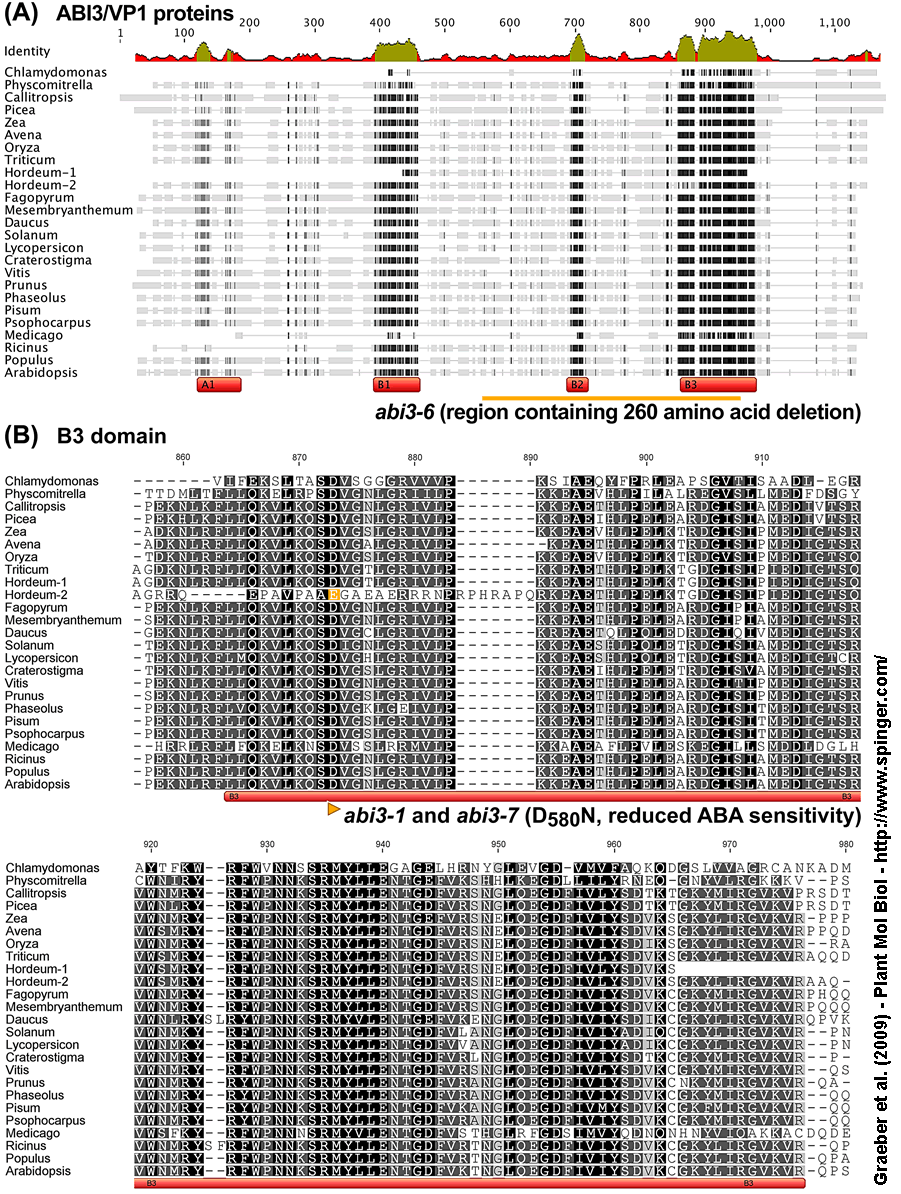
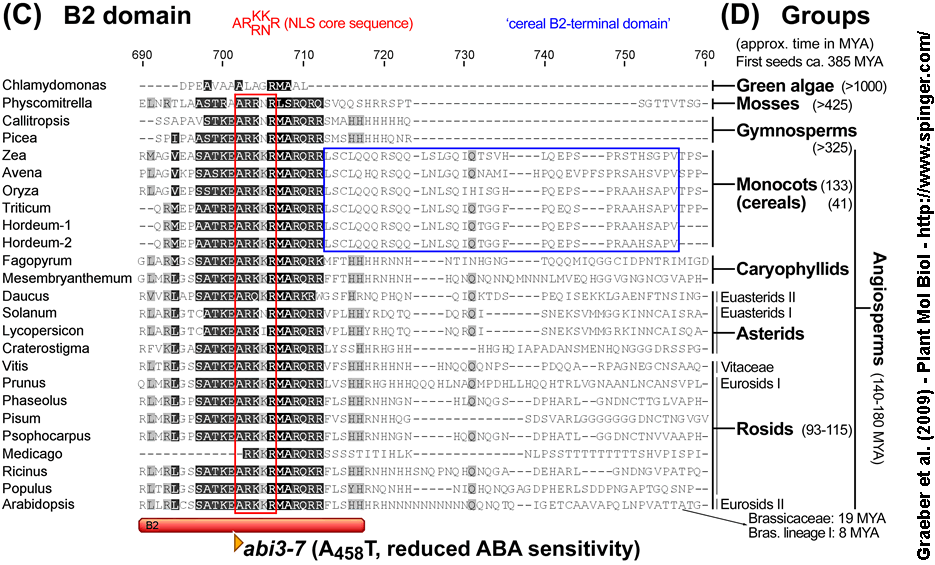
Figure 1. Alignment of deduced amino acid sequences of ABI3/VP1 (ABA INSENSITIVE3 / VIVIPAROUS1) proteins from plants. Alignments are comparisons of the
(A) entire proteins showing the overview of the domain structure (with known domains A1, B1, B2, B3) and the regions of identity (visualized by the identity plot on top of panel A and by dark areas in the individual sequences),
(B) B3 domain and the
(C) B2 domain amino acid sequences.
(D) The plant groups (green algae, mosses, gymnosperms and angiosperms) including the divergence time estimates of their crown subgroups (in 'million years ago', MYA) based on the current view of deep-level relationships (Franzke et al. 2009; Soltis et al. 2008; Wang et al. 2009).
ABI3/VP1 protein sequences (NCBI accession number): Chlamydomonas reinhardtii CrABI3/VP1-like (XP_001693653.1), Physcomitrella patens PpABI3 (XP_001752973.1), Callitropsis nootkatensis CnABI3 (CAC19186.1), Piceae abies PaVP1 (AAG22585.1), Zea mays ZmVP1 (NP_001105540.1), Avena fatua AfVP1 (CAA04553.1), Oryza sativa OsVP1 (EAY76922.1), Triticum aestivum TaVP1 (CAB91108.1), Hordeum vulgare HvVP1 ('Hordeum-1' AAO06117.1, 'Hordeum-2' CAD24413.1), Fagopyrum esculentum FeVP1 (BAC78904.1), Mesembryanthemum crystallinum McVP1 (BAA28779.1), Daucus carota DcABI3 (BAA82596.1), Solanum tuberosum StABI3-like (CAC84597.2), Lycopersicon esculentum LeABI3 (AAW84252.1), Craterostigma plantagineum CpVP1 (CAA04184.1), Vitis vinifera Vv(CAO63796.1), Prunus avium PaABI3 (AAQ03210.1), Phaseolus vulgaris PvABI3-like (BAB96578.1), Pisum sativum PsABI3-like (BAC10553.1), Psophocarpus tetragonolobus (BAD42433.1), Medicago truncatula MtABI3-like (ABD32571.1), Ricinus communis (EEF41288.1), Populus trichocarpa PtABI3 (CAA05921.1), Arabidopsis thaliana AtABI3 (CAA48241.1). Selected mutations of the Arabidopsis ABI3 gene and conserved amino acids of a nuclear localization signal (NLS) core sequence are indicated.
| Article in PDF format (872 KB) Abstract of PMB 2009 |
|
|
|
The Seed Biology Place |
Webdesign Gerhard Leubner 2000 |